
My Dog Has A Lump Lipoma In Dogs
A lipoma is a very common, usually benign, mass most often located under a dog's skin. It is made up exclusively of fat cells. Lipomas can occur at any age, though they are more common in middle-aged to older dogs. Aging dogs may develop many lipomas over the course of their lifetime. These tumors are usually benign, or non-cancerous, and.

Lipoma in Dogs A GoodRx Guide to Canine Lipoma GoodRx
1. A Healthy Diet. Ensuring your dog's diet is well-balanced and nutritious can assist in supporting their ideal weight and avoiding the buildup of unwanted fat. Avoid processed foods, grains, sugars, or artificial additives that can trigger inflammation and promote tumor growth.

Dog Cysts! Lipomas, Cysts and Blackhead Removal YouTube
Lipomas are common types of tumors seen in dogs. A lipoma is a benign fatty mass that can be found anywhere on a dog's body, typically under the skin. They usually feel soft and moveable and rarely cause pain or discomfort for the dog. Lipomas can be surgically removed if they interfere with your dog's mobility or comfort, grow rapidly, or.
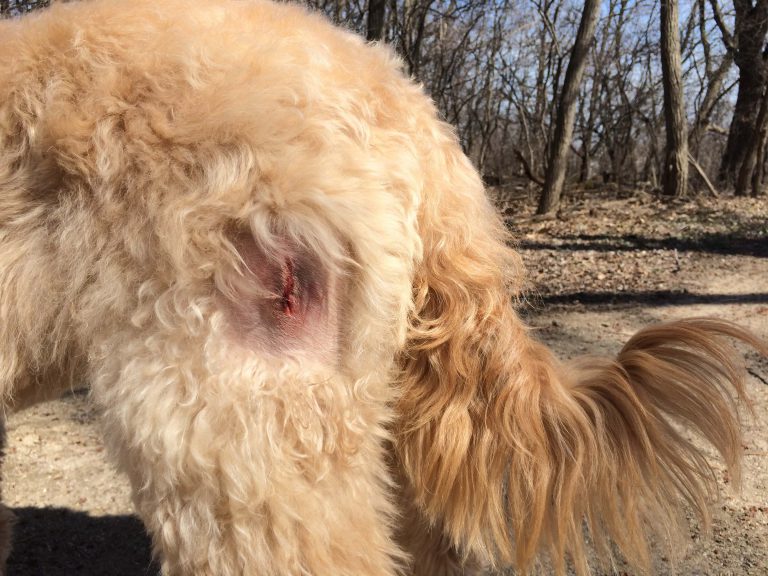
My Dog Has A Lump Lipoma In Dogs
Generally, lipomas are slowly growing masses that are found underneath the skin. The mass can either be found in the subcutaneous space between the skin and muscle, or sometimes even within the muscle. Rarely a lipoma can be found within the skin or dermis. Infrequently lipomas can be found within the chest or abdomen.

Dog Fatty Tumors How to Tell and Treat Lipomas At Home YouTube
Clinical Symptoms of Lipomas in Dogs. Soft, often slightly moveable, nonpainful lump under the skin. If the lipoma is in the chest, you may notice your dog breathing faster, shallow, or coughing. Lipomas on the spleen are rare, but they can grow and rupture the splenic capsule leading to internal bleeding. If this occurs, you may notice pale.

Canine Lipomas Noncancerous Tumors
A dog lipoma is a common soft tissue tumor that grows in fat cells. The fatty tumors are often movable, not painful to the touch, and can be unattached to the surrounding tissues (muscle underneath or skin above). If attached, it is known as an infiltrative dog lipoma. The most common site for lipomas is the subcutaneous fat right under a dog.

Large lipoma in a dog YouTube
Typically dogs do not show any discomfort or irritation from a lipoma unless the lipoma is located in an area that hinders movement or normal bodily functions. There are certain breeds that are more prone to developing lipomas, including the Labrador Retriever, Beagle, Doberman Pinscher, Miniature Schnauzer, American Cocker Spaniel, Weimaraner.

How To cure Lipoma In Dogs petswithlove.us
Overview. Lipomas are benign (noncancerous), freely movable, relatively slow-growing, fat-filled tumors that are quite common in dogs, especially older ones. They are soft, easily manipulated, and located just under your dog's skin. While they can develop anywhere, they are most commonly found on your dog's undercarriage, in the chest or.

Lipoma in Dogs Fatty Tissue Tumors And What They Mean For Your Pet
Lipomas are given two major classifications non-infiltrative and infiltrative. Noninfiltrative lipomas are also known as simple lipomas. They are located beneath the skin and are quite easy to remove. Infiltrative lipomas in dogs on the other hand tend to grow into adjacent tissues. They invade fascia and muscle tissue to a greater degree than.

Lipomas in Dogs 5 Natural Remedies YouTube
One type of lump is called a lipoma. Lipomas are tumors made of fat cells. They form when fat cells build up at a faster rate in a particular area. Their size depends on how many fat cells the tumor stores. If a dog is overweight, lipomas are likely to be bigger. They should shrink if the dog loses weight. Lipomas are usually benign, meaning.

This picture was taken of a Lipoma (tumor) before and after removal by
Recovery and Management of Dog Lipomas. If you and your veterinarian opt for a conservative approach of monitoring your dog's lipoma versus surgical removal, pay careful attention to monitoring the size and growth rate of the lipoma. Record the size at least every six months and document it with photos and measurements.
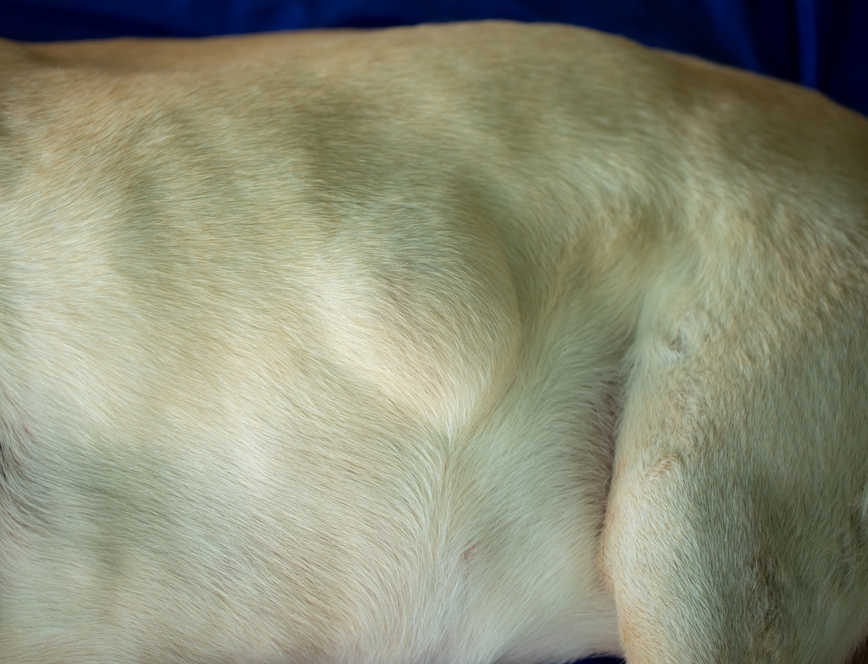
Lipomas in Dogs What They Look Like [With Pics] and What to Do
A lipoma is a common benign (i.e. non-cancerous) tumor of adipocytes, which are fat cells. Lipomas usually have well-defined boundaries and typically do not invade the underlying tissue. They are located commonly in dogs just below the skin of the trunk and limbs of the dog's body. However, in some cases, a dog may have a lipoma in the chest.
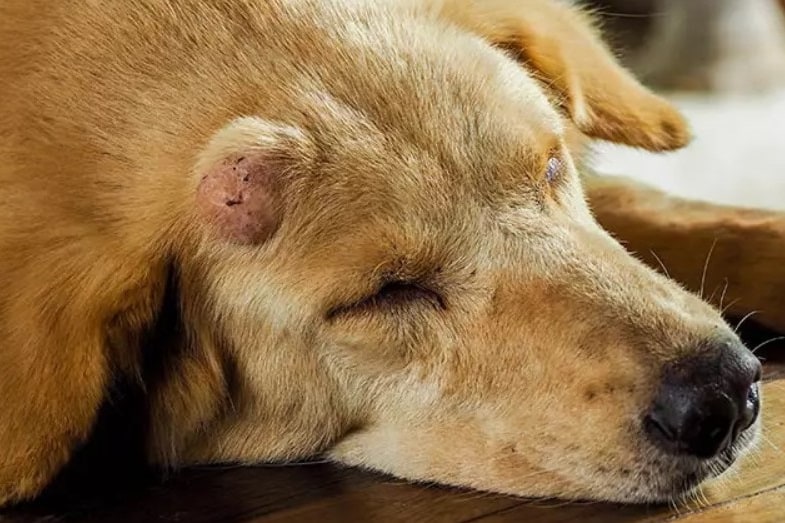

Dog Lipoma, Fatty Tumors, and Cysts (With Pictures) Skin Care Geeks
A lipoma is a benign tumor made up of fat cells that is common in middle-aged or older dogs. It is typically soft and movable, and should not cause pain or discomfort. But if it is large or located in an area where it interferes with movement, it may need to be removed surgically. Of all the benign growths your pup might develop as they age.

Lipomas in Dogs An Unconventional Approach Dr. Magda
Fatty lumps, like the one on this dog, can grow extremely large. Lipomas are harmless lumps that start in fat cells stored in tissue around the body and are not usually painful. They accumulate more fat as they grow and are more likely in middle-aged to elderly dogs. The size the lump will grow to depends on how much fat the lipoma stores, but.

Extirpación quirúrgica de lipomas gigantes en perros Veterinarian Center
Lipomas. These fatty tumors appear as soft, round lumps of flesh beneath the skin. They're made up entirely of fat cells and are always benign, or non-cancerous. Lipomas are usually found in.
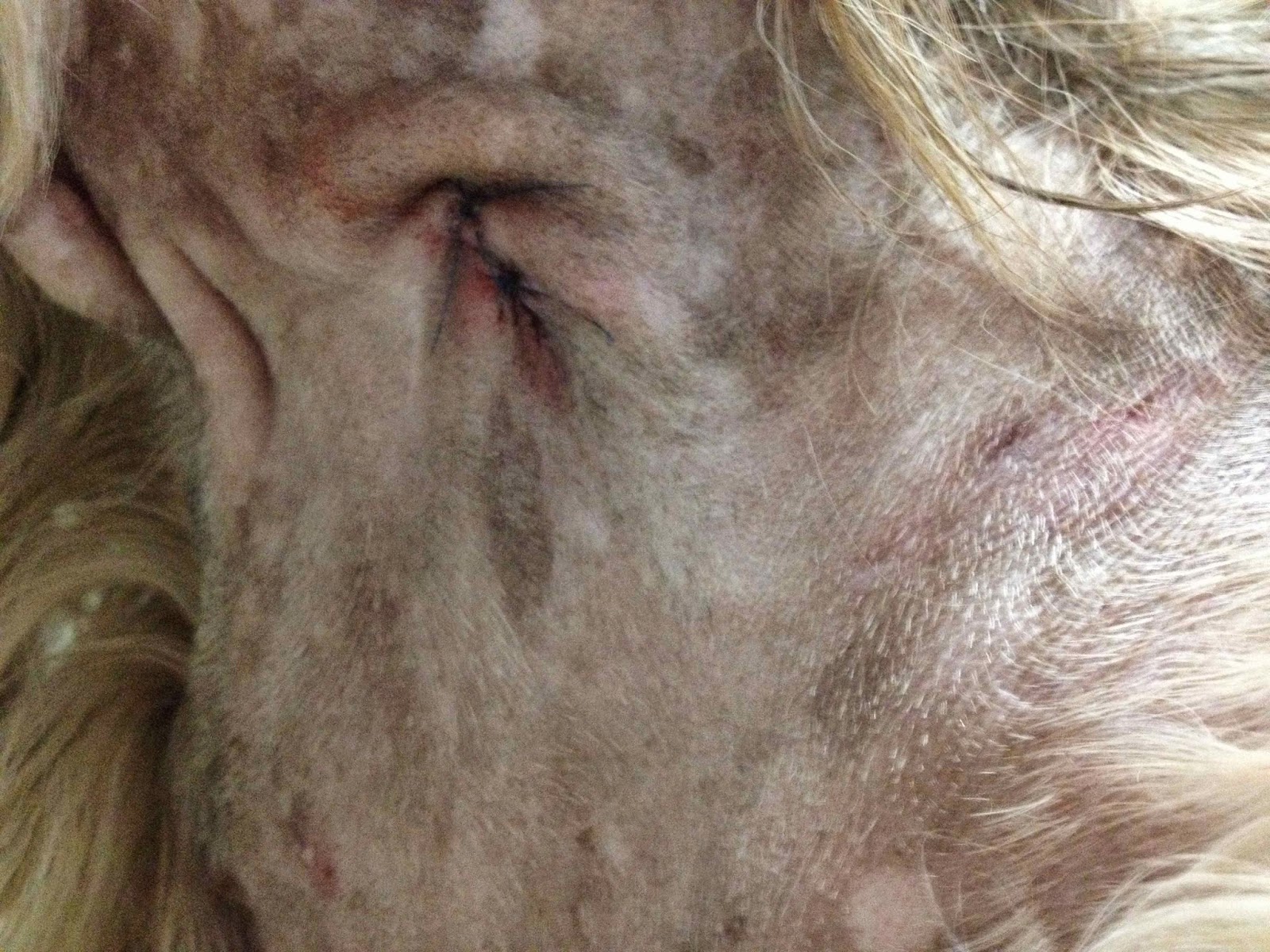
My dog those darned lipomas scare us
Oftentimes they are hereditary, although several breeds are prone to them. Sometimes they can be caused by physical trauma. Below, are some common causes of lipomas. 1. Poor Diet. It is thought that carbohydrates, preservatives, and toxins found in processed dog food can contribute to fatty tumors. 2.